There is a lot of information out there about the endocannabinoid system and a lot of it involves very technical and scientific language. It took me a while to figure out how to explain what I learned into layman terms so that the average person could understand it (especially myself).
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a collection of cells and neurotransmitter receptors, located primarily in our central nervous system. It serves as a cell-signaling system that regulates our bodies to maintain homeostasis. If homeostasis becomes imbalanced, it may lead to disease or death.
THE ENDOCANNABINOID SYSTEM, SIMPLIFIED
Let’s start with a simple breakdown of the definition of the word “endocannabinoids”:
Endocannabinoids are cannabis-like substances that are naturally produced inside of our bodies. Endo” is short for the word “endogenous” and literally means “within”. “Cannabinoid” derives from the word “cannabis”. The endocannabinoid system is often referred to by its acronym “ECS”.
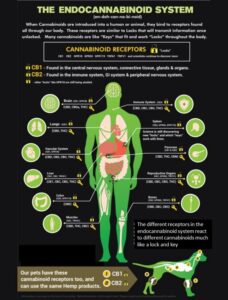
The endocannabinoid system interacts with chemical compounds that scientists labeled as cannabinoids. After cannabinoids interact with the CB receptors and carry out their functions, they are broken down by different enzymes.
Studies have shown these interactions help regulate and balance key bodily functions.
- appetite
- pain sensation
- mood
- memory
- neuroprotection
- sensory perception
- metabolism
- neutralizing harmful free radicals
IN A NUTSHELL: WHAT ARE CANNABINOIDS?
So far, scientists have identified two types of cannabinoids: endocannabinoids and phytocannabinoids.
Endocannabinoids are produced naturally within the human body. Phytocannabinoids are secreted by cannabis plants. THC and CBD are the most well known and researched phytocannabinoids. Researches have so far identified almost 200 phytocannabinoids secreted by the cannabis plant.

THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) is the most legendary phytocannabinoid known to mankind because of its psychoactive properties. It will get you “high” or “stoned”.
CBD and other recently discovered phytocannabinoids (CBG, CBC, CBN, and CBL) are non-psychoactive and have been clinically proven to provide medicinal benefits without the “high” effect.
CBD VS THC COMPARISON TABLE
Cannabidiol (CBD) is predominant in the hemp plant. Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is predominant in the marijuana plant. CBD will not get you high. THC will get you high. CBD is available without a doctor prescription. Medicinal marijuana containing high levels of THC requires a prescription.
| CBD | THC |
| Non-psychoactive (No “high” effect) | Psychoactive (Will get you “high”) |
| Extracted from hemp plant | Derived from marijuana plant |
| Contains less than 0.3% THC | Usually contains from 15% or 30% THC |
| Legal in all 50 states | Legal in a few states in the District of Columbia |
| No doctor prescription required | Must have doctor prescription, if medicinal |
| Can reduce appetite | Can stimulate appetite |
| May help cancer patients | May help cancer patients |
| Can increase mental focus and clarity | Can reduce cognitive abilities |
| Can help reduce anxiety | Can induce panic attacks |
| Does not cause paranoia | Can cause paranoia |
| May reduce episodes of seizures | May reduce episodes of seizures |
| Can provide relaxation without drowsiness | Can cause extreme drowsiness |
| No known serious side effects | Can cause nausea and vomiting |
In the table above comparing CBD and THC, you may notice that CBD has more positive benefits listed than THC.
However, much medical research has shown THC in marijuana cultivated for medicinal purposes to have therapeutic benefits for a variety of ailments in clinical lab studies.
Most of the negatives assigned to THC in the chart above are experienced by recreational users that consume marijuana beyond moderation.
Some people are sensitive to THC and may experience negative side effects such as those listed in the CBD vs. THC table above. There are generally two types of people that are sensitive to THC whether it comes from marijuana or hemp:
- Those whose bodies have an allergic hypersensitivity to THC and may experience mild to severe side effects with even low doses. These folks are especially sensitive to edibles such as gummies and chocolate bars that contain THC.
- Those who suffer from cannabis use disorder, a medical diagnosis for problematic marijuana use. According to medical researchers, roughly 10% of 193 million THC consumers worldwide are plagued with cannabis use disorder.
Now, let’s think about the logic of this. If 10% of 193 million THC consumers (marijuana users) around the world become burdened with cannabis use disorder, that means roughly 90% of THC consumers experience positive benefits from their consumption of THC products without any problematic issues. Right?
5 POSITIVE THERAPEUTIC BENEFITS OF MARIJUANA THC
May relieve and prevent migraine headaches
While further research needs to be conducted, some current research shows that marijuana may not only lessen the agonizing pain of headaches and migraines but may actually prevent them from happening in the first place.
From January 2010 to September 2014, a trio of University of Colorado medical researchers performed a study of 121 adults diagnosed with migraine headaches. Out of the 121 participants in the study, all of which used marijuana daily to help them prevent migraine headache attacks, reported the number of migraine headaches they experience monthly were reduced by 50%.
May reduce stress and relieve tension and anxiety
A team of medical researchers from the University of Chicago and University of Illinois – Chicago performed a study measuring the effects of marijuana’s therapeutic effectiveness for stress relief.
The study involved 42 healthy volunteers ranging from 18 years old to 40 years old. The volunteers were divided into three control groups:
- A low dose group that received a 7.5 mg THC capsule
- A moderate dose group that received a 12.5 mg THC capsule
- A placebo group that received a capsule containing no THC
Here’s the results:
The low dose group reported less stress than the placebo group.
The moderate dose group reported negative moods. In addition, they described the tasks they had to perform during the study as challenging or threatening.
In general, the study indicated the stress levels of the volunteers actually were relieved with a lower dose of THC. However, those volunteers that consumed higher doses of THC experienced increased stress and anxiety.
May be an effective treatment for glaucoma
According to CDC.gov, glaucoma is the leading cause of blindness in the United States and affects about 3 million Americans.
In the early 1970s, the National Eye Institute (NEI) supported research studies that showed marijuana helped lower the intraocular pressure in people who suffered from glaucoma. However, some participants in those studies also experienced an increased heart rate and a decrease in blood pressure.
May decrease PTSD symptoms
The Veterans Administration (VA) estimates that one-third of all veterans suffer from PTSD.
In 2021, the Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies (MAPS) conducted a placebo-controlled, double-blinded study that found that marijuana users experienced a greater decrease in the severity of their PTSD symptoms versus those participants that received a placebo.
The study also found that marijuana users were 2.5 times more likely to be undiagnosed with PTSD versus those who did not use marijuana.
May reduce inflammation and relieve pain
Chronic inflammation is a major risk factor that contributes to many different kinds of diseases including depression and arthritis.
In a 2009 study, researchers found that marijuana can decrease the production of cytokine and chemokine, two chemical compounds that can trigger inflammation.
In a 2013 FDA-approved double-blind, placebo-controlled study, researchers found that marijuana users consuming low doses of marijuana THC experienced a 30% reduction in neuropathic pain compared to participants that received a placebo.
CLINICAL ENDOCANNABINOID DEFICIENCY
Clinical endocannabinoid deficiency (CED) is a theory postulated by Dr. Ethan Russo, a board-certified neurologist. In research studies conducted by Dr. Russo, he found evidence that an endocannabinoid deficiency was closely linked to migraines, fibromyalgia, and irritable bowel syndrome.
As mentioned, the ECS works to keep our bodies in a constant state of internal temperature (homeostasis) as we experience fluctuations in our external environment such as extreme hot and cold weather.
Basically, when endocannabinoids – the cannabinoids that our bodies naturally produce – interact with the CB receptors, the ECS becomes a molecular signaling system that regulates a broad range of biological processes to maintain homeostasis.
When a deficiency occurs in the endocannabinoids that our bodies naturally produce, a condition occurs that is known as Clinical Endocannabinoid Deficiency (CED).
Reasons why a deficiency in endocannabinoids in our bodies can occur include:
- Our bodies do not produce enough cannabinoid receptors
- Our bodies do not synthesize enough endocannabinoids
- Endocannabinoids are broken down by an abundance of enzymes in our bodies
- Ingesting foods and medications that interfere and slow down the ECS signaling system
When someone is diagnosed with Clinical Endocannabinoid Deficiency, phytocannabinoids such as THC and CBD have been clinically proven to stimulate and support the endocannabinoid system thus returning it to a properly functioning molecular signaling system that restores homeostasis and provides relief from a multitude of physical and mental ailments and health conditions.